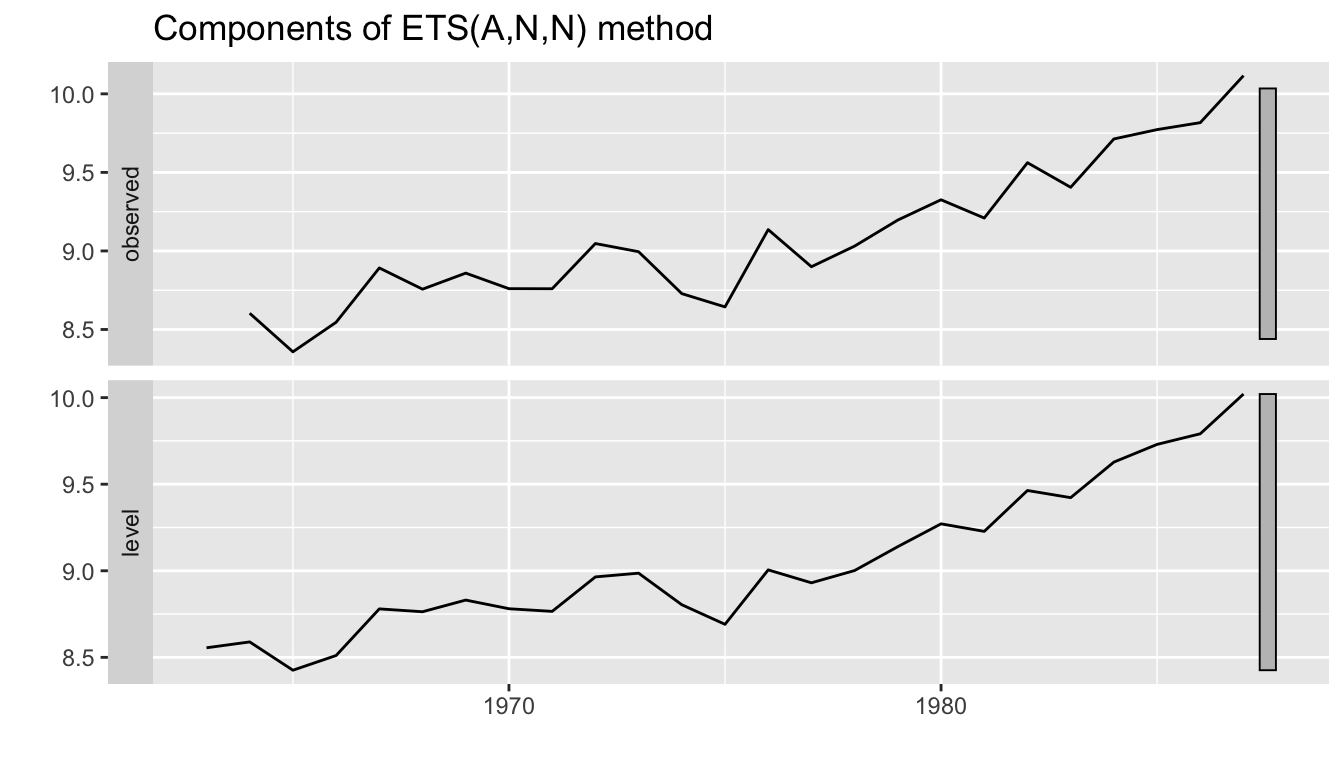
4.2 ets() function
The ets() function in the forecast package fits exponential smoothing models and produces forecasts from the fitted models. It also includes functions for plotting forecasts.
Load the data by loading the FishForecast package.
Fit the model.
model="ANN" specifies the simple exponential smoothing model.
Create a forecast for 5 time steps into the future.
Plot the forecast.
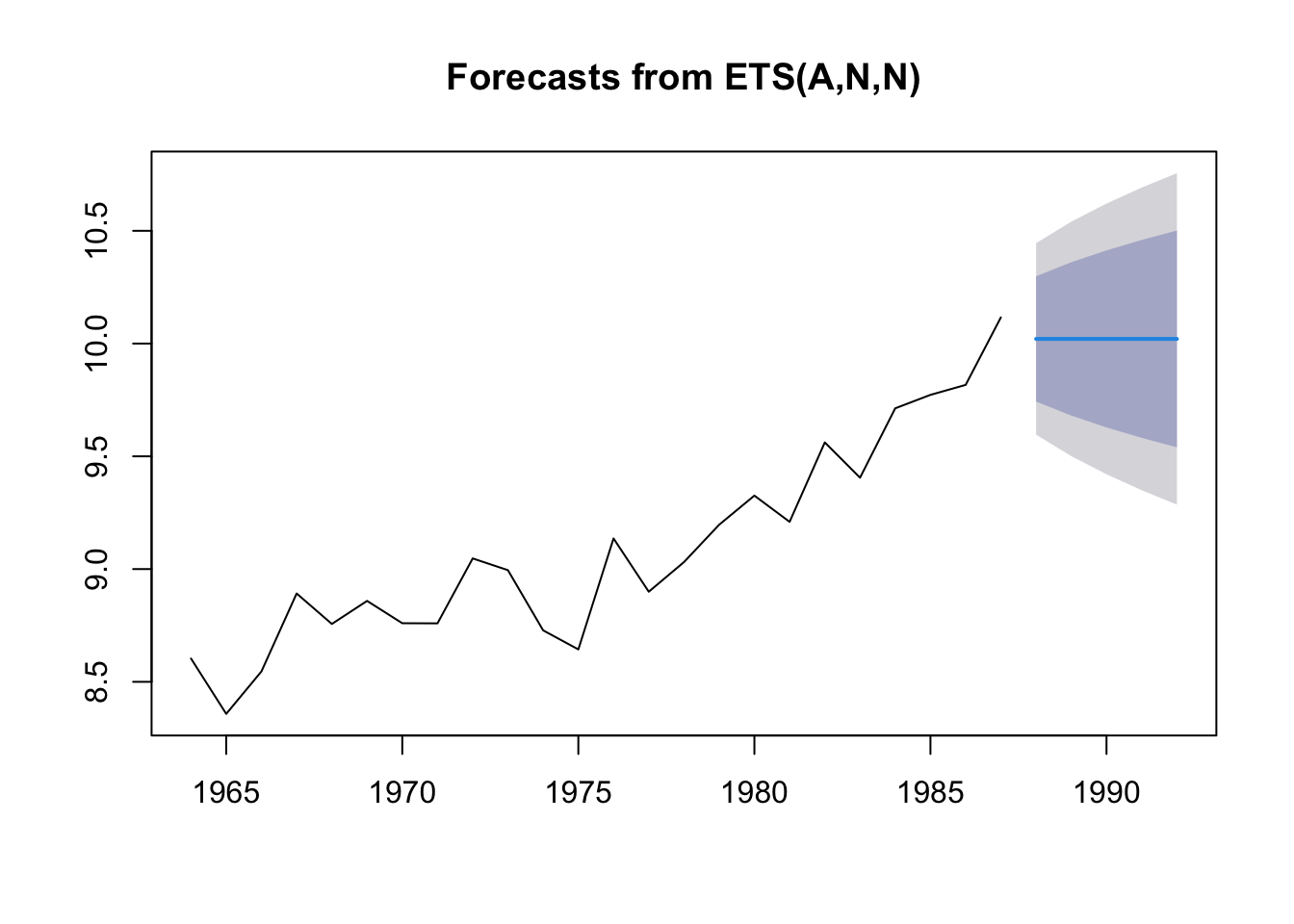
Look at the estimates
## ETS(A,N,N)
##
## Call:
## forecast::ets(y = anchovy87ts, model = "ANN")
##
## Smoothing parameters:
## alpha = 0.7065
##
## Initial states:
## l = 8.5553
##
## sigma: 0.2166
##
## AIC AICc BIC
## 6.764613 7.964613 10.2987754.2.1 The weighting function
The first coefficient of the ets fit is the \(\alpha\) parameter for the weighting function.
alpha <- coef(fit)[1]
wts <- alpha*(1-alpha)^(0:23)
plot(1987:1964, wts/sum(wts), lwd=2, ylab="weight", xlab="", type="l")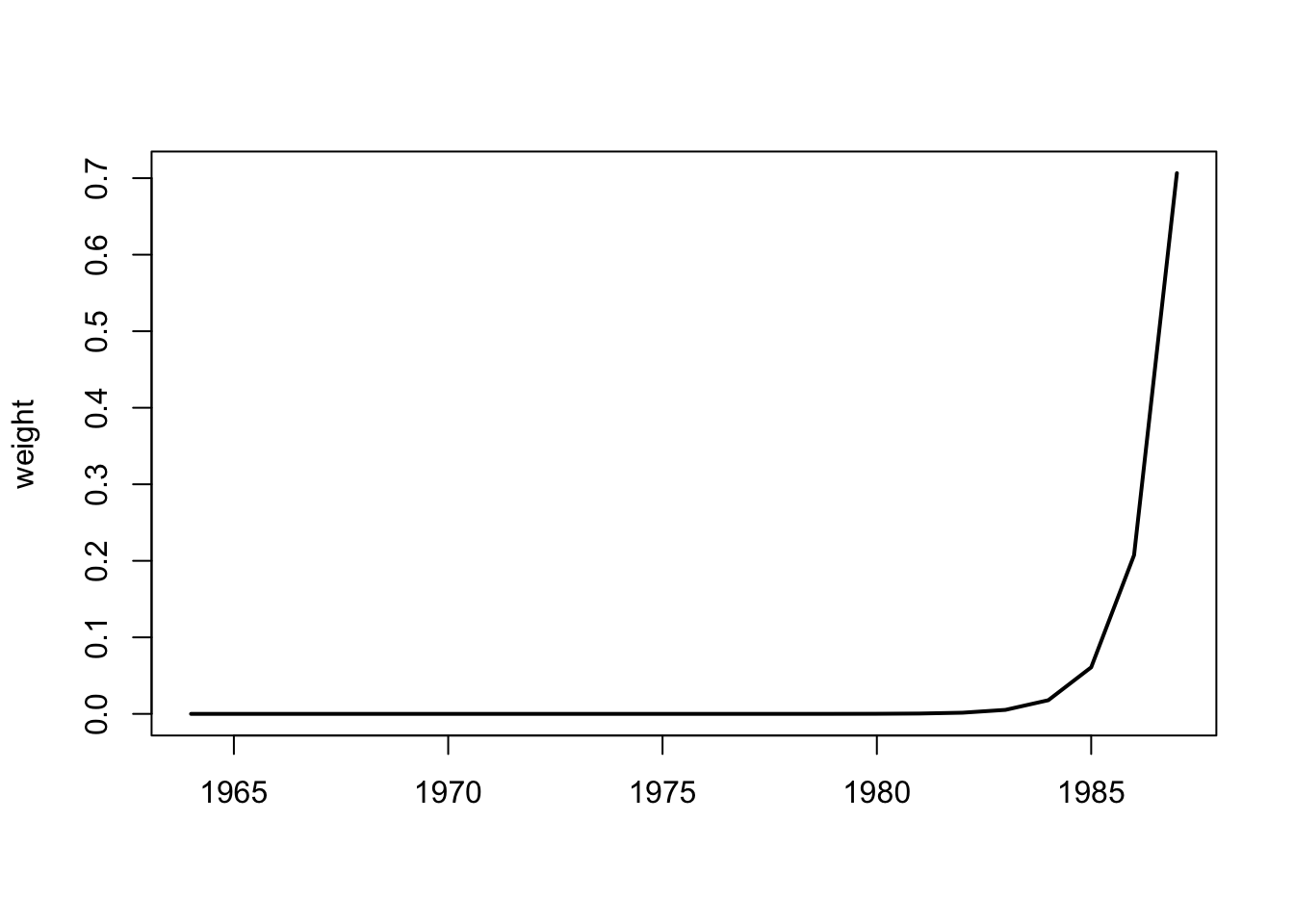
(#fig:ann.weighting)Weighting function for the simple exponential smoothing model for anchovy.